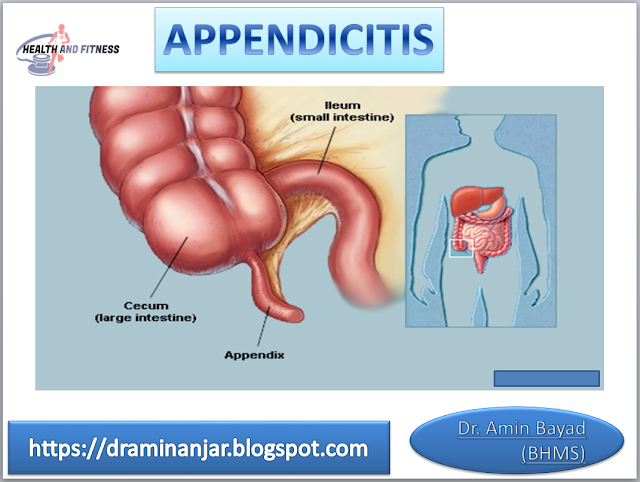
Psoriasis : Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment | 2019
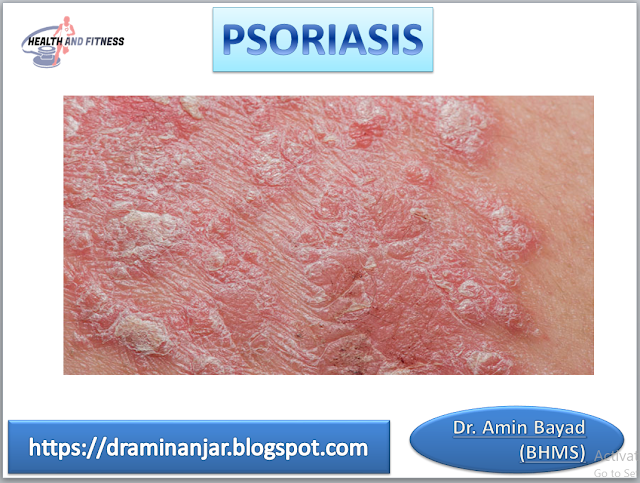
Psoriasis is an autoimmune inflammatory condition of the skin that causes rapid accelerate of skin cell. The skin of psoriasis is looked like scales, red and patchy which are extremally itchy, painful and some time discharge may come out.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that reoccurs many time, so because of this reason, our main aim is to control the growth of the skin.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition so, there is no complete cure is possible but you may control your symptoms by some lifestyle changes and medication.
According to the appearance of scales and their location psoriasis is dived in different types.
Prevalence
The number of cases of psoriasis is increasing day by day. That mainly due to our diet habit. In the USA 8 million people have psoriasis.
According to the world psoriasis day consortium, 2 to 3% (125 million) of the total population worldwide have psoriasis.
Age:- Psoriasis can be developed at the age of 15 to 45 but can develop at any age.
Psoriasis Causes
There is still research are ongoing for particular causes of psoriasis. Some scientist indicates that the main cause of psoriasis is autoimmune but some say that there is a combination of autoimmune with trigger factor or lifestyle. The main problem is with T-cell of our body.
Main Function of T-cell in our body is to fight again foreign cell or substance to protect our body.
In psoriasis, because of Autoimmune disease T-cell mistakenly attack our healthy skin cell. So, this overreaction of T-cell causes more production of skin cell to that particular part of the body that leads to more T-cell, WBC and RBC are conjoint together at affected part of the body. More cell of skin needs more blood supply and so because of more blood supply that affected part becomes red, swollen and sometimes pus may come out.
Triggers of psoriasis
Triggers of psoriases also play an important role. The symptoms of psoriasis become worsen due to some triggers.
- Another autoimmune disease ( HIV)
- Strep Infection Know more
- Smocking
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
- Beta-blocker medication, Anti-malarial Drug
- Incised wound, cut, surgery
- Vit. D Deficiency
Risk Factor of Psoriasis
1.Stress
2.Family History
3.Obesity
4.Smocking
5.Infection
2.Family History
3.Obesity
4.Smocking
5.Infection
Types of psoriasis
➤ Plaque Psoriasis is the commonest form of psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis can occur anywhere in the body with the lesion of one or few. Characteristics of plaque psoriasis are dry, redness, and silvery scales which are painful.
➤ Guttate Psoriasis affects mainly to young adult and children. Guttate Psoriasis is always followed by some bacterial infection like strep throat. Peculiarities of Guttate Psoriasis is a small, scaling lesion on the trunk, arm, and legs.
➤ Inverse Psoriasis affects mainly on the covered area like armpit, under breast, groin, genital. Because of friction and sweating. Inverse psoriasis characteristics are smooth, redness, inflamed skin. Inverse psoriasis is followed by any fungal infection.
➤ Pustular psoriasis is common among in adult. which localized a smaller part of the body like hand and feet. Pustular psoriasis looks like pus-filled blister, inflamed and redness of the skin.
➤ Erythrodermic Psoriasis is due to stopping of existing psoriasis treatment. Erythrodermic psoriasis is very rare but life-threatening diseases because of its complication such as heart failure and pneumonia. Characteristic of erythrodermic is undefined edges, peeling of the skin, severe itching and pain.
Psoriasis symptoms are very characteristic different from person to person. Symptoms of psoriasis mainly depend on the type of psoriasis. some common symptoms are as follow
➜ Redness around the skin
➜ Severe itching
➜ Painful lesion
➜ Plaques on the affected area
➜ Burning sensation
➜ Dryness and cracked skin
➜ Discoloration and pitting of nails
➜ Inflammation and stiffness of joints
The physician can make some physical examination to detect any redness, plaque, and dead skin to identify psoriasis.
The physician may advise for biopsy test to rule out bacterial infection and confirmation of diagnosis.
There are a number of complications of psoriasis are as follow:-
➤ Guttate Psoriasis affects mainly to young adult and children. Guttate Psoriasis is always followed by some bacterial infection like strep throat. Peculiarities of Guttate Psoriasis is a small, scaling lesion on the trunk, arm, and legs.
➤ Inverse Psoriasis affects mainly on the covered area like armpit, under breast, groin, genital. Because of friction and sweating. Inverse psoriasis characteristics are smooth, redness, inflamed skin. Inverse psoriasis is followed by any fungal infection.
➤ Pustular psoriasis is common among in adult. which localized a smaller part of the body like hand and feet. Pustular psoriasis looks like pus-filled blister, inflamed and redness of the skin.
➤ Erythrodermic Psoriasis is due to stopping of existing psoriasis treatment. Erythrodermic psoriasis is very rare but life-threatening diseases because of its complication such as heart failure and pneumonia. Characteristic of erythrodermic is undefined edges, peeling of the skin, severe itching and pain.
Psoriasis Symptoms
Psoriasis symptoms are very characteristic different from person to person. Symptoms of psoriasis mainly depend on the type of psoriasis. some common symptoms are as follow
➜ Redness around the skin
➜ Severe itching
➜ Painful lesion
➜ Plaques on the affected area
➜ Burning sensation
➜ Dryness and cracked skin
➜ Discoloration and pitting of nails
➜ Inflammation and stiffness of joints
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
The physician can make some physical examination to detect any redness, plaque, and dead skin to identify psoriasis.
The physician may advise for biopsy test to rule out bacterial infection and confirmation of diagnosis.
Complication Of Psoriasis
There are a number of complications of psoriasis are as follow:-
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Stress
- Diabetes know more here
- High Blood Pressure
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular disease
- Metabolic syndrome
- Parkinson's disease
- Kidney disease
Treatment of Psoriasis
There is the number of treatment method are available for psoriasis. Treatment of psoriasis mainly depends on the type of psoriasis. For better understanding, I will divide into 3 part which is as follow.
1.Topical Treatment
Your physician prescribes some topical ointments for relieving burning sensation, inflammation, and slow down of growth of skin cell. There is a wide range of topical ointment are freely available.
- Corticosteroids:- This is commonest and frequently used corticosteroids for the treatment of psoriasis. They treat mild to moderate psoriasis. Topical corticosteroids are short term therapy because if you use for a longer time than your skin become resistant to that particular steroids and on later stage they not respond properly.
- Retinoids:- This is derivatives of Vitamin A. This is useful for the slow down growth of skin cell. They also reduce inflammation and itching
- Vitamin D:- Most of the Physician prescribes Vit.D with corticosteroids. Vitamin D helps in slowing down of growth skin cell, remove scales, and plaques of psoriasis.
- Salicylic Acid is widely used in the tropical treatment of any skin disease. Salicylic acid is freely available on medical store with or without combination. The physician may prescribe salicylic acid with corticosteroids. Salicylic acid removes the skin cell and decreases the scaling of the skin.
- Moisturizer is add on therapy in psoriasis. However, moisturizer alone can not treat psoriasis but they can help in reducing itching and dryness.
2. Systemic Medication
In severe psoriasis or if a large area is infected than a physician can advise taking orally or injectable medication.
- Methotrexate is used to decrease the production of new skin cell and heal inflammation. The physician starts methotrexate with a low dose and gradually increase the dose. There is some side effect of methotrexate is liver damage and damage to bone marrow, because of this side effect the production of RBC and WBC also decrease.
- Retinoids are derivatives of Vitamin A which is used for severe psoriasis but you should also know the side effect of retinoids i.e, hair loss and inflammation of lips. Retinoids should not use in pregnant women or planning to be pregnant because retinoids can cause the birth defect. If women are on treatment on retinoids than she should avoid pregnancy for at least 3 years.
- Cyclosporine is similar to methotrexate both work on to suppress the immune system. Long therapy of cyclosporine should be avoided because of its side effect. Cyclosporine suppresses the immune system and that's why our body becomes more prone to infection, cancer, and high blood pressure.
- Biologics:- These are a group of biologics medicine to treat severe psoriasis. Some are as follow 1. Infliximab 2. adalimumab 3. etanercept 4. apremilast 6.golimumab etc. Most are injectable and has a high risk of side effect.
3. Light therapy:- In this therapy, can use natural as well as artificial ultraviolet light therapy. Natural light therapy includes sunlight and in artificial include ultraviolet A and B., we can use both combinations or singly.
4. Home remedies and lifestyle changes for psoriasis:- Lifestyle changes may help in to improve damaged skin and you feel better. There is some point to improve in life for psoriasis.
- Use moisturizer
- Bath daily
- Expose to some part of the skin to sunlight
- Avoid Triggers of Psoriasis
- Avoid Alcohol drinking Addiction killer herbal
Home remedies for psoriasis
Natural remedies for psoriasis can be used along with traditional treatment. Here are some natural home remedies that help along with traditional treatment.
1)Apple Cider vinegar Buy Best Vinegar
2)Aloe Vera Best buy here
3)Capsaicin
4)Ots
5)Tea tree oil Buy here
6)Turmeric
7)Dead sea salt Best sea salt
8)Mahonia aquifolium
List of homeopathic remedies for psoriasis
1. Arsenic alb
2. Graphites
3. Psorinum
4. Arsenic Iodatum
5. Sulphur
6. Petroleum
7. Sepia succus
8. Merc sol
Dr. Amin Bayad
(BHMS)